Discover the Egyptian Museum of Cairo: A Journey Through History
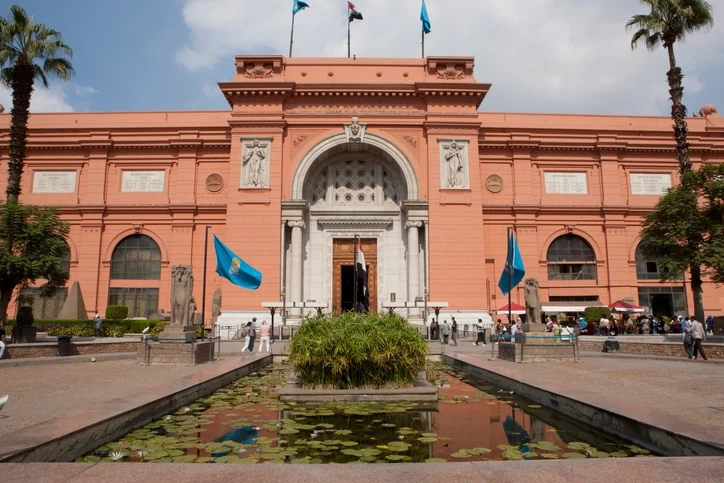
The Egyptian Museum of Cairo, also known as the Museum of Egyptian Antiquities, is a world-renowned institution that houses the most extensive collection of ancient Egyptian artifacts. Located in the heart of Cairo’s Tahrir Square, this iconic museum showcases over 120,000 artifacts spanning thousands of years, offering visitors an unparalleled glimpse into the rich and fascinating history of ancient Egypt. From the legendary treasures of Tutankhamun to colossal statues, delicate jewelry, and intricate papyrus scrolls, the museum is an essential destination for history enthusiasts, archaeologists, and tourists alike.
The History of the Egyptian Museum
The Foundation of the Museum
The origins of the Egyptian Museum trace back to the 19th century when Egypt’s rich archaeological heritage faced extensive looting. To preserve these invaluable relics, the Egyptian government, under Khedive Isma’il Pasha, established the first antiquities service in 1835. The collection initially found a home in several locations, including Boulaq and Giza, before being transferred to its current neoclassical-style building in 1902.
The Significance of Tahrir Square’s Iconic Museum
The museum’s location in Tahrir Square places it at the heart of Cairo’s cultural and political history. Over the years, it has stood as a symbol of Egypt’s deep connection to its past, attracting millions of visitors who seek to explore the country’s ancient heritage.
The Treasures of the Egyptian Museum: Must-See Artifacts
Tutankhamun’s Golden Mask: The Crown Jewel of the Museum
The most famous exhibit in the Egyptian Museum is the breathtaking gold mask of Pharaoh Tutankhamun. Discovered in 1922 by British archaeologist Howard Carter, this stunning artifact, crafted from 11 kilograms of solid gold, represents the pinnacle of ancient Egyptian craftsmanship. It adorned the mummified face of the boy king and remains one of the most iconic symbols of ancient Egypt.
The Royal Mummies Hall: A Glimpse into the Afterlife
The museum’s Royal Mummies Hall houses the preserved remains of some of Egypt’s most legendary pharaohs, including Ramses II, Hatshepsut, and Seti I. These well-preserved mummies offer a fascinating insight into the embalming techniques of the ancient Egyptians and the grandeur of their burial rituals.
The Narmer Palette: The Birth of an Empire
The Narmer Palette, one of the museum’s oldest artifacts, dates back to around 3100 BCE and is considered a crucial piece of evidence in understanding the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt. This intricately carved slate depicts King Narmer wearing the crowns of both regions, symbolizing his rule over a unified Egypt.
The Statue of Khafre: The Pharaoh’s Eternal Presence
Another must-see artifact is the diorite statue of Pharaoh Khafre, who ruled during the Fourth Dynasty. The statue, with its lifelike details and protective falcon of Horus behind the king’s head, exemplifies the artistic mastery of ancient Egyptian sculptors.
The Amarna Collection: The Revolutionary Art of Akhenaten
The museum also features artifacts from the Amarna Period, a unique artistic and religious movement initiated by Pharaoh Akhenaten. These artifacts, including sculptures and reliefs of the royal family, showcase a distinctive style that broke away from traditional Egyptian art.
The Museum’s Layout
The Ground Floor: The Foundation of Ancient Egypt
The ground floor of the museum is dedicated to Egypt’s Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, and New Kingdom artifacts. Visitors can explore statues, stone sarcophagi, hieroglyphic inscriptions, and various objects used in daily life.
The Upper Floor: The Treasures of the Pharaohs
The upper floor houses the most celebrated pieces, including the treasures of Tutankhamun, royal jewelry, and items from the Valley of the Kings. It also features objects from the Greco-Roman period, reflecting Egypt’s cultural fusion over the centuries.
Visiting the Egyptian Museum: Practical Information
Location and How to Get There
The Egyptian Museum is conveniently located in Tahrir Square, making it easily accessible by taxi, metro, or organized tours. Visitors can take the Cairo Metro and stop at Sadat Station, which is within walking distance of the museum.
Opening Hours and Ticket Prices
Opening Hours: The museum is open daily from 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM.
Ticket Prices: General admission tickets are reasonably priced, with discounts available for students and Egyptian citizens. Additional fees apply for the Royal Mummies Hall and photography permits.
Best Time to Visit
For a more comfortable experience, visiting early in the morning or during the off-peak seasons (spring and autumn) is advisable. Weekends and holidays tend to be more crowded.
The Future of the Egyptian Museum: The Grand Egyptian Museum
While the Egyptian Museum remains an essential cultural landmark, a new, state-of-the-art institution—the Grand Egyptian Museum (GEM)—is set to open near the Giza Pyramids. The GEM will house many of the artifacts currently displayed in the Egyptian Museum, including the full collection of Tutankhamun’s treasures.
Frequently Asked Questions About The Egyptian Museum
1. What is the most famous artifact in the Egyptian Museum?
The most famous artifact is the golden mask of Tutankhamun, an exquisite piece of craftsmanship that symbolizes ancient Egyptian opulence.
2. How long does it take to explore the museum?
A comprehensive visit takes around 3 to 4 hours, though history enthusiasts may spend even longer admiring the extensive collection.
3. Are guided tours available at the museum?
Yes, guided tours are available and highly recommended for a deeper understanding of the exhibits. Audio guides and private tour options are also offered.
4. What is the difference between the Egyptian Museum and the Grand Egyptian Museum?
The Egyptian Museum in Tahrir Square is the current home of Egypt’s vast collection of antiquities. The Grand Egyptian Museum, opening soon near the Giza Pyramids, will offer a more modern exhibition space with expanded displays.
5. Can visitors take photos inside the museum?
Photography is allowed in most areas of the museum, though a small fee may be required. Flash photography is prohibited to protect the artifacts.
Conclusion: A Must-Visit Destination for History Lovers
The Egyptian Museum of Cairo is an irreplaceable treasure trove of ancient history, offering an unforgettable journey through time. Whether you're marveling at the golden mask of Tutankhamun, standing before the statues of legendary pharaohs, or admiring intricately preserved artifacts, this museum is a testament to the grandeur and sophistication of ancient Egyptian civilization. If you're planning a trip to Cairo, visiting this iconic museum should be at the top of your itinerary.